Continuous Systems (continuous_systems)¶
-
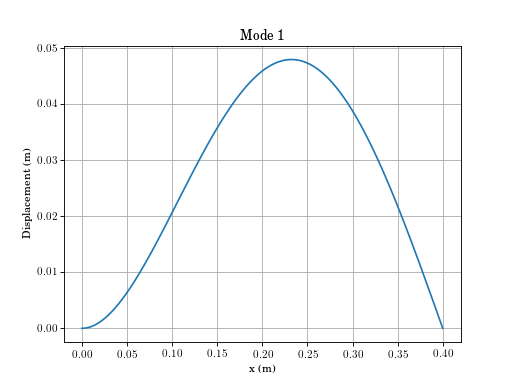
continuous_systems.euler_beam_modes(n=10, bctype=3, npoints=2001, beamparams=array([7.3100e+10, 8.4375e-09, 2.7470e+03, 4.5000e-04, 4.0000e-01]))[source]¶ Mode shapes and natural frequencies of Euler-Bernoulli beam.
- Parameters
- n: int, numpy array
highest mode number or array of mode numbers to return
- bctype: int
bctype = 1 free-free bctype = 2 clamped-free bctype = 3 clamped-pinned bctype = 4 clamped-sliding bctype = 5 clamped-clamped bctype = 6 pinned-pinned
- beamparams: numpy array
E, I, rho, A, L, Young’s modulus, second moment of area, density, cross section area, length of beam
- npoints: int
number of points for returned mode shape array
- Returns
- omega_n: numpy array
array of natural frequencies
- x: numpy array
x coordinate
- U: numpy array
mass normalized mode shape
Examples
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
-
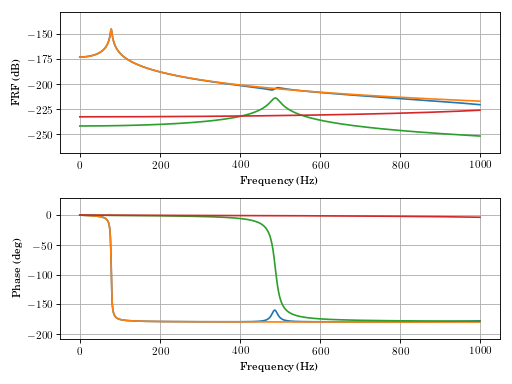
continuous_systems.euler_beam_frf(xin=0.22, xout=0.32, fmin=0.0, fmax=1000.0, zeta=0.02, bctype=2, npoints=2001, beamparams=array([7.3100e+10, 8.4375e-09, 2.7470e+03, 4.5000e-04, 4.0000e-01]))[source]¶ Frequency response function fo Euler-Bernoulli beam.
- Parameters
- xin: float
location of applied force
- xout: float
location of displacement sensor
- fmin: float
lowest frequency of interest
- fmax: float
highest frequency of interest
- zeta: float
damping ratio
- bctype: int
bctype = 1 free-free bctype = 2 clamped-free bctype = 3 clamped-pinned bctype = 4 clamped-sliding bctype = 5 clamped-clamped bctype = 6 pinned-pinned
- beamparams: numpy array
E, I, rho, A, L, Young’s modulus, second moment of area, density, cross section area, length of beam
- npoints: int
number of points for returned mode shape array
- Returns
- fout: numpy array
array of driving frequencies (Hz)
- H: numpy array
Frequency Response Function
Examples
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)